With summer comes an increase in sports and outdoor activities, which often lead to an increase in injuries of our joints and back. This newsletter will focus mainly on extremity (arm/leg) injuries; back pain will be discussed in a later issue.
Extremity injuries can be due to direct trauma, twisting forces to our joints, or from repetitive use of our arms and legs. These injuries come in three different types:
- Sprains involve a stretching or tearing of a ligament in a joint (ligaments are the tough bands of fibrous tissue that connect two bones together). Wrist and ankle sprains are very common injuries. Mild sprains involve mainly stretching of the ligament and usually heal within 1-2 weeks. More severe sprains are due to a partial or even complete tear of a ligament and can take several weeks to heal; some may even require surgery.
- A strain is a stretching or tearing of muscle or tendon. A tendon is a fibrous cord of tissue that connects muscles to bones. Strains often occur in the lower back and in the hamstring muscle in the back of your thigh. Most strains also usually heal within a week or two.
A fracture means a broken bone, and it almost always requires medical attention.
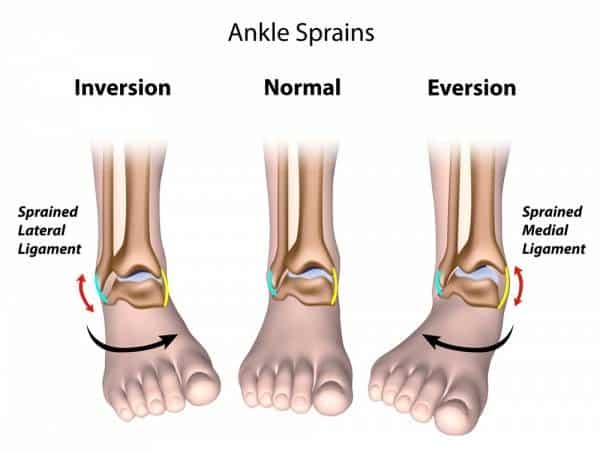
How is a sprain or strain or fracture diagnosed?
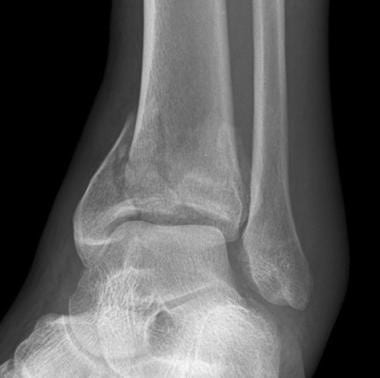
Sprains, strains, and fractures can all cause severe pain, swelling, and bruising. You may even here a “pop” or a “snap” sound during the injury. It is often difficult for most people to tell what type of injury they may have, but a physical exam by a doctor can usually differentiate between a sprain, strain, or fracture. If your doctor has any concern about a fracture, then an XRay will be performed. In a few cases, a small fracture may not show up on the first XRay, and your doctor may recommend a repeat XRay or CT scan or MRI. The XRay below shows an example of an ankle fracture.
What should you do if you get injured?
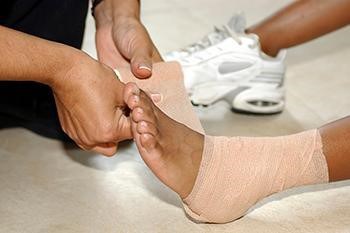
Initial treatment for sprains, strains, and fractures includes rest, ice, compression and elevation. Medical professionals refer to these as “RICE” guidelines:
- R = Rice
- I = Ice (and Ibuprofen)
- C = Compression (eg, using an ACE bandage as in the picture below)
- E = Elevation
If your pain or swelling is particularly severe, or if you cannot walk, you should see your doctor or visit Access Now Urgent Care.
What is the treatment for these injuries?
Treatment of Sprains and Strains:
Mild sprains and strains can be successfully treated at home. Your doctor will usually recommend that you follow the “RICE” instructions and take pain medication such as Ibuprofen (Advil or Motrin). Occasionally a splint (a temporary partial cast) is applied to immobilize the joint; this helps accelerate the healing process. Crutches may also be recommended for foot, ankle, and knee injuries. Severe sprains and strains may sometimes require surgery to repair torn ligaments, muscles or tendons.
Treatment of Fractures:
If you are diagnosed with a fracture, you will initially be placed in a splint. Your doctor will likely refer you to a specialist such as an Orthopaedic Surgeon or Podiatrist. Some fractures require a cast for the bone to fully heal, while others may require an operation. As fractures tend to be very painful, your doctor will likely give you a prescription for a strong pain reliever